
A robust and efficient system to exchange health information between various entities in the US healthcare industry is critical for providing the best possible patient care. The 21st Century Cures Act, passed in 2016, paved the way for the Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement (TEFCA), designed to improve nationwide health information sharing.
At the heart of TEFCA lies Qualified Health Information Networks (QHINs), a critical strategy component to enhance interoperability across healthcare providers, health information networks, and health information exchanges. As the nation moves toward a more connected and cohesive healthcare system, understanding the workings of QHINs and TEFCA becomes essential for stakeholders seeking to optimize their roles in this collaborative ecosystem.
This article delves into the implementation and impact of QHINs under TEFCA in the US healthcare industry, examining the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders, potential benefits and challenges, and the broader implications for data sharing and patient care.
Implementation of QHINs under TEFCA
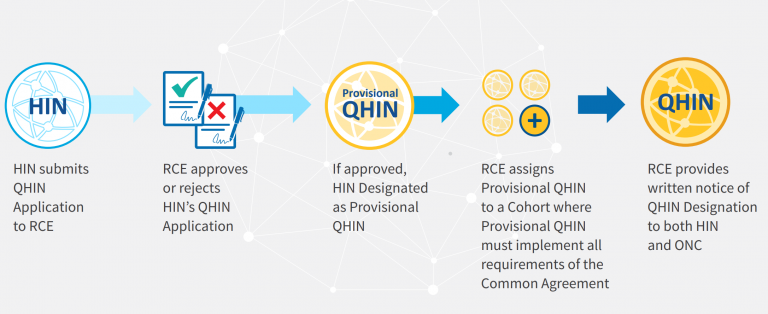
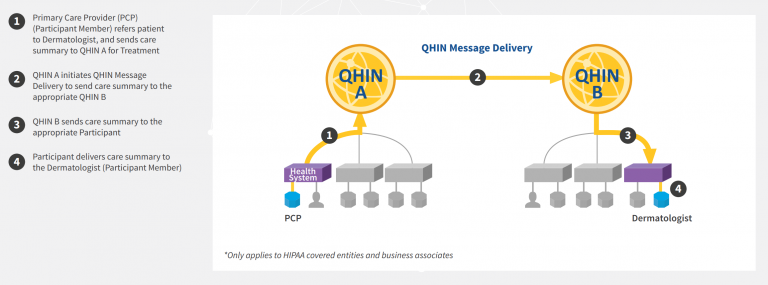
The implementation of QHINs under TEFCA is a multi-stage process that involves collaboration between various stakeholders. TEFCA aims to create a single “on-ramp” for nationwide health information exchange by connecting multiple networks and allowing them to exchange data more efficiently and securely.
The Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) is vital in developing the Trusted Exchange Framework (TEF), which outlines the principles and guidelines for secure health information exchange. The Common Agreement, which will be iterated by the Recognized Coordinating Entity (RCE), complements the TEF by establishing the specific technical and legal requirements for participating entities.
Healthcare providers, health information networks, and health information exchanges must meet the requirements outlined in the Common Agreement to become QHINs. Once designated as QHINs, they can participate in the nationwide exchange of electronic health information, enabling seamless and secure sharing of patient data. The impact of QHINs on TEFCA will be seen in several areas:
Improved interoperability
QHINs will facilitate standardized, secure, and efficient data sharing among health IT systems by adopting a common set of policies, practices, and technical standards. This improved interoperability will help healthcare providers and organizations access and exchange patient information more easily, leading to better care coordination and reducing duplication of services.
Increased data access
QHINs will enable healthcare providers to access a broader array of health information, including clinical, administrative, and financial data. This access can improve decision-making by providing a more comprehensive picture of a patient’s health history and care, leading to better patient outcomes.
Enhanced privacy and security
TEFCA establishes a common set of privacy and security requirements for QHINs, ensuring that patient data is protected in compliance with federal and state laws. QHINs must adhere to these requirements to participate in the nationwide exchange, which helps to maintain trust in the system and protect sensitive health information.
Support for public health
QHINs can provide valuable data to support public health efforts, such as monitoring the spread of infectious diseases or tracking the effectiveness of public health interventions. By facilitating the flow of health information, QHINs can contribute to better population health management and help public health agencies respond to emerging health issues more effectively.
Reduced healthcare costs
By promoting efficient and accurate data exchange, QHINs can help reduce the costs associated with duplicate tests, procedures, and treatments. Additionally, improved access to information can lead to better care coordination and more appropriate care delivery, potentially reducing overall healthcare costs.
Increased patient engagement
TEFCA encourages QHINs to support patient access to their health information, empowering individuals to become more involved in their care and make better-informed decisions about their health.
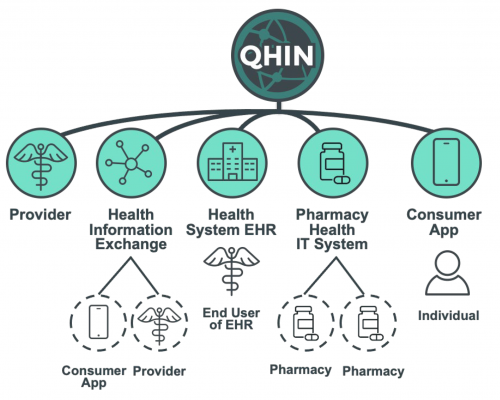
Roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders
The successful implementation and operation of QHIN under TEFCA require the collaboration and commitment of various stakeholders in the US healthcare industry. This section explores the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders, highlighting their contributions to the initiative’s overall success.
Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC)
The ONC, a part of the US Department of Health and Human Services, is responsible for coordinating nationwide efforts to implement and advance health information technology and the electronic exchange of health information. Key responsibilities of the ONC concerning QHINs under TEFCA include:
Developing the Trusted Exchange Framework (TEF), which sets the principles and guidelines for health information exchange.
Overseeing the Recognized Coordinating Entity (RCE) responsible for creating and maintaining the Common Agreement.
Monitoring and evaluating the progress of TEFCA implementation and its impact on nationwide health information exchange.
Recognized Coordinating Entity (RCE)
The RCE is a private or public organization selected by the ONC to develop, maintain, and update the Common Agreement, which outlines the specific technical, legal, and policy requirements for QHINs. The RCE’s responsibilities include:
Collaborating with stakeholders to develop the Common Agreement in alignment with the principles of the Trusted Exchange Framework.
Managing the process of onboarding and qualifying health information networks as QHINs.
Ensuring compliance with the Common Agreement and monitoring the performance of QHINs.
- Updating and revising the Common Agreement as needed to adapt to changing industry needs and technology advancements.
Qualified Health Information Networks (QHINs)
QHINs are healthcare providers, health information networks, and health information exchanges that meet the requirements outlined in the Common Agreement. Their responsibilities encompass:
Implementing the necessary technologies and processes to meet the requirements of the Common Agreement.
Ensuring the secure and efficient exchange of electronic health information with other QHINs and authorized participants.
Complying with the privacy and security regulations outlined in the Common Agreement, as well as applicable federal and state laws.
Continuously improving their performance, contributing to the growth and development of the nationwide health information exchange.
Healthcare providers
Healthcare providers, such as hospitals, clinics, and individual practitioners, will play a crucial role in the success of QHIN under TEFCA. Their role would include:
Adopting and integrating health information technologies that support interoperability and information exchange with QHINs.
Ensuring the privacy and security of patient data during the exchange process.
Participating in the health information exchange to contribute to improved patient care and outcomes.
Encouraging patient engagement and empowering patients to access and manage their health information.
By understanding and fulfilling their roles and responsibilities, these key stakeholders contribute to the creation of a more connected, efficient, and patient-centric healthcare system through the implementation of QHIN under TEFCA.
Potential benefits and challenges of QHIN under TEFCA
QHINs will play a crucial role in achieving TEFCA’s goals by providing the infrastructure and framework for more effective, efficient, and secure health information exchange. As QHINs continue to develop and expand their capabilities, the potential positive impacts on healthcare delivery, patient outcomes, and the healthcare system as a whole are likely to grow.
Improved patient care
By facilitating the seamless and secure exchange of electronic health information, QHINs will enable healthcare providers to access comprehensive patient data, ultimately resulting in better-informed decisions and improved patient outcomes.
Enhanced interoperability
QHINs will promote interoperability by standardizing the exchange of health information, making it easier for healthcare providers, health information networks, and health information exchanges to communicate effectively, irrespective of their technological differences.
Empowered patients
QHINs would allow patients to access their health information across multiple providers easily, enabling them to make informed decisions about their healthcare and engage more actively in managing their health.
Cost reduction
The nationwide health information exchange facilitated by QHINs can lead to reduced costs associated with redundant tests, administrative tasks, and delays in care resulting from a lack of information.
Public health and research advancements
QHINs will enable unprecedented aggregation and analysis of health data on a larger scale, which can contribute to advancements in public health and medical research.
While the implementation of QHINs under TEFCA promises significant benefits for the US healthcare industry, it also presents various challenges that must be addressed. By acknowledging and addressing these challenges, stakeholders can work together to ensure the initiative’s success and realize the potential benefits for patients, providers, and the healthcare system as a whole.
Privacy and security concerns
As health information exchange becomes more widespread, ensuring the privacy and security of patient data remains a crucial concern. The TEFCA and Common Agreement include provisions to address these issues, but continued vigilance and commitment from all stakeholders are necessary.
Technology adoption and integration
Healthcare organizations may face challenges in adopting and integrating the necessary technologies to comply with the requirements of the Common Agreement. Smaller organizations, particularly, may struggle with limited resources and technical expertise.
Resistance to change
As with any significant change in the healthcare industry, some stakeholders may resist the shift towards a nationwide health information exchange. Encouraging participation and addressing concerns will be essential to implementing QHINs successfully.
Data quality and standardization
Ensuring data quality and standardization is critical for the success of health information exchange. Inconsistencies in data format, coding, and terminology may hinder the effective exchange of information and impact patient care.
Legal and regulatory compliance
Navigating the complex landscape of federal and state laws and regulations surrounding health information exchange can be challenging. Healthcare organizations must ensure they comply with applicable laws, such as HIPAA, in addition to the requirements of the Common Agreement.
Broader implications for data sharing and patient care
TEFCA’s implementation of QHINs will have far-reaching implications for data sharing and patient care in the US healthcare industry. As the initiative continues to gain traction, it has the potential to transform the landscape of health information exchange, fostering collaboration and innovation, promoting data-driven decision-making, enhancing patient engagement, spurring innovation, and addressing health disparities.
Facilitating collaboration
QHINs will encourage collaboration among healthcare providers, health information networks, and health information exchanges by establishing a common framework for exchanging health information. This collaborative environment can lead to the sharing of best practices, improved coordination of care, and the development of innovative solutions to address the challenges faced by the healthcare industry.
Promoting data-driven decision making
With seamless access to comprehensive patient data, healthcare providers can make more informed decisions based on real-time information. This data-driven approach can lead to more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes. Moreover, the aggregation and analysis of health data on a larger scale can contribute to advancements in public health and medical research.
Enhancing patient engagement
The initiative will empower patients to access their health information across multiple providers easily, enabling them to take a more active role in managing their health. This enhanced patient engagement can lead to better adherence to treatment plans, improved patient satisfaction, and more effective preventive care.
Fostering innovation
The increased availability and exchange of health data through QHINs can spur innovation in the healthcare industry. Healthcare organizations can develop new tools and solutions for disease detection, treatment optimization, and patient monitoring by leveraging advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. Furthermore, the secure and efficient exchange of health information can encourage the development of innovative applications and services that improve patient care and streamline healthcare operations.
Addressing health disparities
As QHINs will enable the exchange of health information on a national scale, the initiative has the potential to address health disparities by ensuring that all patients, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status, have access to high-quality care. By facilitating the sharing of health information across different providers, QHINs can help reduce barriers to care and reduce health disparities in underserved communities.
Conclusion
Through enhanced interoperability, improved patient access to health information, cost reduction, and the promotion of data-driven decision-making, QHINs under TEFCA can pave the way for a more connected, efficient, and patient-centric healthcare ecosystem. However, the success of this initiative hinges on the collective efforts of all stakeholders in addressing the challenges posed by privacy and security concerns, technology adoption and integration, resistance to change, data quality and standardization, and legal and regulatory compliance.
As a leading Seattle-based healthcare software development company, Itirra recognizes TEFCA’s transformative potential for the US healthcare industry. The nationwide health information exchange facilitated by QHIN promises to revolutionize how healthcare providers, health information networks, and health information exchanges collaborate, share data, and ultimately deliver patient care.
At Itirra, we are committed to supporting the successful implementation of TEFCA and QHINs by developing innovative software solutions that facilitate secure, efficient, and seamless health information exchange. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, we believe that the collaborative environment fostered by QHINs will drive advancements in patient care, research, and technology, ultimately contributing to a healthier future for all Americans.

