
In the world of healthcare data exchange, the Health Level Seven International (HL7) messaging standard has long been the go-to choice for seamless communication among diverse healthcare systems. As the need for efficient, reliable, and secure data sharing continues to grow, understanding the most widely used HL7 message types becomes crucial for healthcare professionals and software developers alike. In this article, we delve into the top HL7 message types that drive the interoperability of healthcare systems and enable informed decision-making in patient care.
Written by a leading Seattle-based healthcare software development company, Itirra, this comprehensive guide aims to provide a clear understanding of the most commonly used HL7 message types and their significance in the healthcare industry. By exploring the purpose and structure of each message type, readers will gain valuable insights into the ways in which these messages facilitate vital information exchange between various healthcare applications and stakeholders.
As the industry moves towards increased digitization and adoption of electronic health records (EHRs), the role of HL7 message types in ensuring smooth communication and data exchange becomes even more essential. This article serves as a valuable resource for healthcare professionals, software developers, and IT managers seeking to enhance their knowledge of the HL7 messaging standard and improve their organization’s data interoperability capabilities.
An overview of HL7 standards
Health Level Seven International (HL7) is a messaging standard that has become integral to the healthcare industry, as it addresses the need for efficient data interoperability and seamless communication among various healthcare systems. Developed by the HL7 organization, this standard has evolved over the years, with the primary goal of enabling diverse applications and systems to exchange clinical, administrative, and financial information in a standardized and secure manner. The importance of data interoperability cannot be overstated, as it allows healthcare providers to access accurate, up-to-date patient information, leading to better decision-making and improved patient outcomes.
HL7 plays a pivotal role in connecting different healthcare systems, allowing for the smooth transfer of information despite variations in technology, software, and hardware. Since its inception, the standard has gone through multiple versions, each designed to improve upon its predecessor.
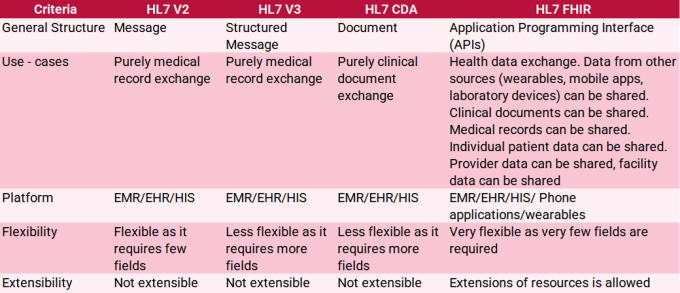
However, the most widely adopted version of the standard is HL7 v2.x, which is known for its flexibility, ease of implementation, and compatibility with various healthcare systems. HL7 v2.x has been extensively used by healthcare organizations, software vendors, and integrators worldwide, solidifying its position as the go-to messaging standard for healthcare data exchange.
The evolution of HL7 has seen the introduction of newer versions and complementary standards, such as HL7 v3 and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR), which are designed to address the growing complexities and demands of modern healthcare systems. While these newer standards offer promising solutions to emerging challenges, HL7 v2.x remains the predominant choice for many organizations due to its widespread adoption, robustness, and familiarity within the industry. It is essential for healthcare professionals and developers to understand the key HL7 message types and their functions to ensure optimal data exchange and seamless communication across diverse healthcare applications.
Top 5 HL7 message types
By developing a deeper understanding of the top HL7 message types and their specific applications within healthcare organizations, professionals can ensure that their systems are capable of exchanging information efficiently. This, in turn, leads to improved patient care, streamlined workflows, enhanced collaboration between healthcare providers, and better overall outcomes.
ADT - Admit, Discharge, and Transfer
ADT messages play a critical role in managing patient movement and administrative processes within healthcare organizations. They communicate a wide range of patient-related events, such as admissions, discharges, transfers, and updates to patient demographics. ADT messages contain multiple segments, with the PID (Patient Identification), PV1 (Patient Visit), and IN1 (Insurance) segments being some of the most crucial.
Within a healthcare setting, ADT messages are used to:
maintain accurate patient records
generate patient lists
manage bed assignments
track patient movement throughout the care process
ORM - Order Message
ORM messages enable the exchange of order-related information, such as laboratory tests, radiology exams, and medication prescriptions. The primary function of an ORM message is to initiate or update an order in the receiving system, allowing healthcare providers to manage and monitor patient care. Key segments in ORM messages include ORC (Order Common) and OBR (Observation Request), which contain essential information about the order, such as the ordering provider, requested service, and urgency.
Common triggers for ORM messages include:
placing new orders
modifying existing orders
canceling orders
acknowledging the receipt of an order
ORU - Observation Result
ORU messages are central to the communication of clinical observation results, including laboratory test results, imaging studies, and other diagnostic findings. These messages ensure that healthcare providers have access to vital patient information, enabling them to make informed decisions about patient care.
The main segments in an ORU message include OBR (Observation Request) and OBX (Observation Result), which contain details about the requested service and the resulting observations. ORU messages are typically triggered by the completion of a test or procedure, with the sending system transmitting the results to the receiving system for further processing.
MDM - Medical Document Management
MDM messages support the management and exchange of clinical documents, such as discharge summaries, clinical notes, imaging reports, and other medical records. These messages are essential for maintaining an accurate, up-to-date, and comprehensive record of patient information across different healthcare systems.
MDM messages consist of segments like TXA (Transcription Document Header) and OBX (Observation Result), which contain metadata about the clinical document and the actual document content. Common scenarios for MDM messages include document creation modification, deletion, and retrieval, ensuring that healthcare providers have access to the most current and relevant patient information.
SIU - Scheduling Information Unsolicited
SIU messages facilitate the communication of appointment and scheduling information between healthcare systems, streamlining patient scheduling, resource allocation, and schedule updates. Key segments in SIU messages include SCH (Schedule Activity Information) and PID (Patient Identification), which contain details about the scheduled activity and patient information. SIU messages can be triggered by events such as appointment creation, modification, cancellation, and confirmation.
In a healthcare setting, SIU messages help manage:
patient appointments
allocate resources such as rooms and equipment
coordinate healthcare provider schedules
What's next for HL7 messaging
As healthcare organizations continue to adopt digital solutions and invest in interoperability, the future of HL7 messaging will be shaped by the emergence of newer standards, technological advancements, and evolving industry requirements. What impact will these developments have on healthcare interoperability?
One of the most promising advances in healthcare interoperability is the emergence of FHIR, a next-generation standard developed by HL7 International. FHIR is designed to enable easier and more efficient data exchange by leveraging modern web technologies and a modular, resource-based architecture. FHIR can complement existing HL7 messaging standards by offering improved flexibility, scalability, and simplicity in managing healthcare data, particularly in the context of web-based applications and mobile devices. FHIR will eventually replace older HL7 standards as healthcare organizations transition to more modern and efficient data exchange methods.
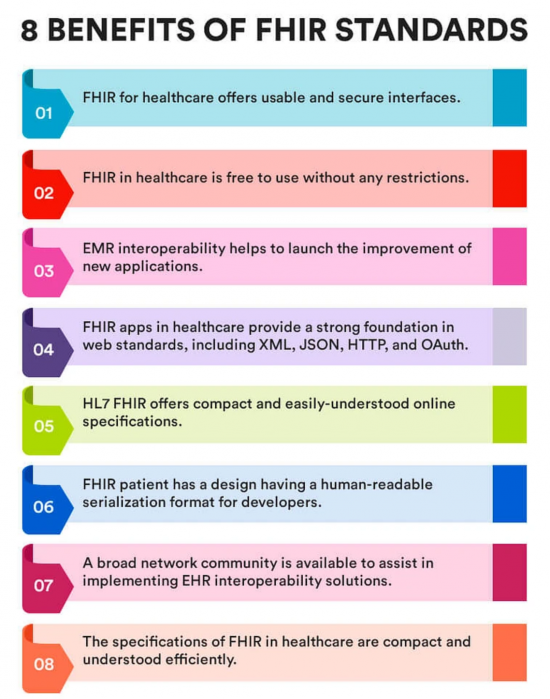
Adopting these emerging technologies, however, presents its own set of challenges and opportunities for healthcare organizations. One of the primary hurdles in implementing FHIR and other next-generation standards is the need to maintain compatibility with legacy systems that still rely on older HL7 messaging protocols.
This may require organizations to invest in integration solutions, such as interface engines or middleware, to ensure seamless communication between systems with different data exchange capabilities. Additionally, healthcare professionals and developers must continually stay informed about the latest advancements in interoperability standards, as well as regulatory changes that may impact their implementation.
Despite these challenges, the adoption of FHIR and other cutting-edge technologies presents a significant opportunity for healthcare organizations to achieve enhanced interoperability, improve patient care, and streamline workflows. By embracing these advances and staying current with the latest developments, healthcare providers can ensure optimal data exchange, seamless communication, and more efficient collaboration across diverse healthcare systems. This, in turn, has the potential to transform the way healthcare information is managed and shared, ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes and overall industry progress.
Conclusion
By delving into the specifics of HL7’s ADT, ORM, ORU, MDM, and SIU messages, industry professionals can gain a deeper appreciation for the role these messaging standards play in facilitating efficient information exchange within diverse healthcare settings. As these message types are widely adopted and integral to healthcare data communication, their proper implementation and management are vital for the seamless functioning of healthcare systems.
Moreover, staying informed about the future of HL7 messaging and emerging standards, such as FHIR, is essential for organizations looking to adapt to the evolving landscape of healthcare interoperability. By embracing cutting-edge technologies and maintaining compatibility with legacy systems, organizations can effectively navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by these advances. This proactive approach ensures that healthcare providers can fully harness the potential of modern data exchange methods to optimize communication, collaboration, and patient care.
As a leading Seattle-based healthcare software development company, Itirra is committed to assisting healthcare organizations in navigating the complexities of HL7 and FHIR messaging standards and related technologies. With our expertise and experience, we can help you implement, optimize, and manage message types to ensure seamless communication and efficient data exchange within your healthcare environment. Your organization can stay ahead of the curve, adapt to the ever-changing healthcare landscape, and ultimately deliver the highest quality of care to your patients.
