
The healthcare industry has long struggled with the interoperability of electronic health information (EHI). Providers, payers, and patients have all faced challenges when trying to share health information between different electronic systems. This has led to a fragmented healthcare landscape, making it difficult for providers to deliver coordinated care and for patients to receive the best possible treatment.
However, the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) has created the Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement (TEFCA) to address these challenges. In this article, we will explore what TEFCA is, how it works, who can participate, and its potential benefits for the healthcare industry. We will also discuss how TEFCA is likely to change the healthcare industry in 2023 and what stakeholders can expect in the years ahead.
TEFCA is a critical initiative that can potentially transform the US healthcare industry. To navigate the technical and legal requirements of TEFCA, healthcare stakeholders may require the expertise of a healthcare software development company like Itirra. Itirra’s team of experienced professionals has a deep understanding of the challenges facing healthcare companies and ways of solving them.
What is TEFCA?
TEFCA stands for the Trusted Exchange Framework and Common Agreement. It is a set of rules and standards designed to improve the sharing of electronic health information (EHI) among healthcare providers, payers, and patients in the United States. TEFCA was created by the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) as part of the 21st Century Cures Act, signed into law in 2016.
TEFCA aims to establish a national health information exchange (HIE) infrastructure that facilitates secure and interoperable data sharing. It consists of two main components: the Trusted Exchange Framework (TEF) and the Common Agreement (CA). The TEF outlines the technical and operational requirements for HIEs to participate in the national network, while the CA establishes the legal and business terms under which HIEs can exchange information.
TEFCA sets forth a set of principles for health information exchange that are designed to ensure patient privacy, security, and data standards. These principles are aligned with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and other relevant regulations.
Who can participate in TEFCA?
TEFCA will be open to a wide range of healthcare stakeholders, including healthcare providers, Health Information Exchanges (HIEs), Health Information Networks (HINs), Health Information Technology (HIT) vendors, payers, and others. These stakeholders will need to meet the technical and legal requirements specified in the TEF and CA to participate in the national HIE infrastructure, including data privacy and security, patient consent and authentication, and technical interoperability requirements.
HINs that apply and comply with the ONC’s health information exchange standards, including using standardized data elements and data exchange protocols, can become a Qualified Health Information Networks (QHIN).
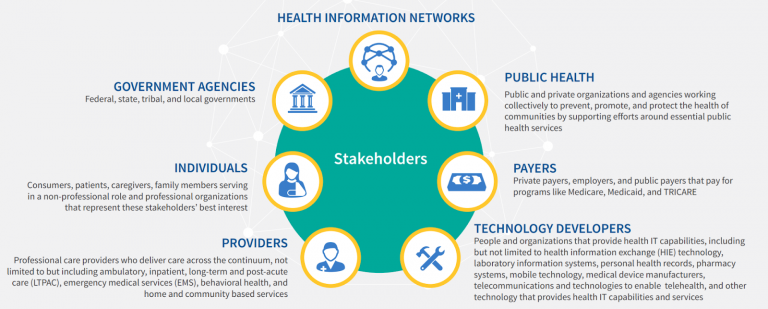
Who is TEFCA for?
TEFCA is designed to benefit a wide range of healthcare stakeholders in the US, including healthcare providers, payers, patients, and technology vendors. TEFCA aims to enable the secure and interoperable exchange of health information between these stakeholders, which can improve patient outcomes, reduce administrative burden, increase efficiency, and facilitate new business models and services.
Healthcare providers
TEFCA will enable healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, physician practices, and other healthcare facilities, to exchange health information with other healthcare stakeholders in a standardized and secure manner. TEFCA aims to allow healthcare providers to access a patient’s complete medical history, resulting in better-informed clinical decision-making. TEFCA can also reduce the administrative burden on healthcare providers by standardizing the exchange of health information, increasing efficiency, and improving patient engagement.
Healthcare payers
Health insurers and government payers will be able to access health information in a standardized format, which can help them better manage risk and improve their cost management strategies. By accessing health information in a standardized format, healthcare payers can identify areas where they can improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. For example, healthcare payers can identify patients at high risk for readmission and provide them with targeted care management services.
Patients
Patients would benefit from the improved quality of care resulting from better-informed clinical decision-making. By enabling healthcare providers to access a patient’s complete medical history, patients can receive more accurate diagnoses and effective treatments. TEFCA can also give patients more control over their health information and easier access to their medical records. Patients can use them to inform their healthcare decisions and share their medical information with other healthcare providers wherever they go.
Technology vendors
By adopting the technical and legal requirements established by TEFCA, Electronic Health Records (EHR) and other healthcare IT vendors can develop comprehensive interoperable IT systems that meet the needs of healthcare providers, payers, and patients. Technology vendors can create standardized interfaces and data translation services to facilitate the secure and interoperable health information exchange between healthcare stakeholders.
How will TEFCA work in 2023?
ONC will select a non-profit entity not affiliated with a QHIN to become a Recognized Coordinating Entity (RCE) to oversee and govern QHINs. TEFCA is expected to establish a national HIE infrastructure that facilitates secure and interoperable data sharing among healthcare stakeholders and publish the Technical Requirements in 2023.
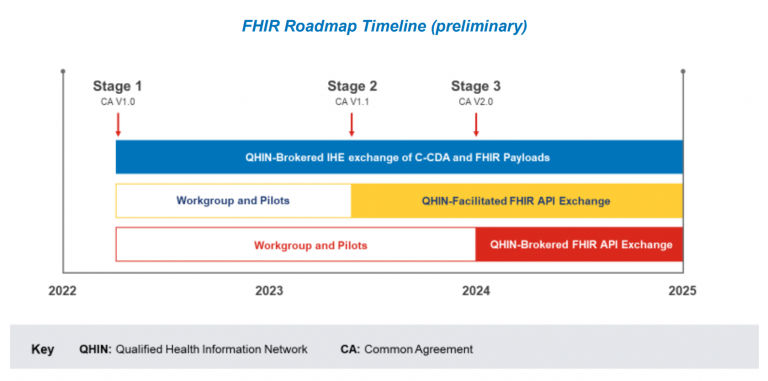
The Technical Requirements are expected to be based on established healthcare data exchange standards, such as Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR). These requirements will specify the technical standards and protocols that healthcare stakeholders must adhere to for secure and interoperable data sharing.
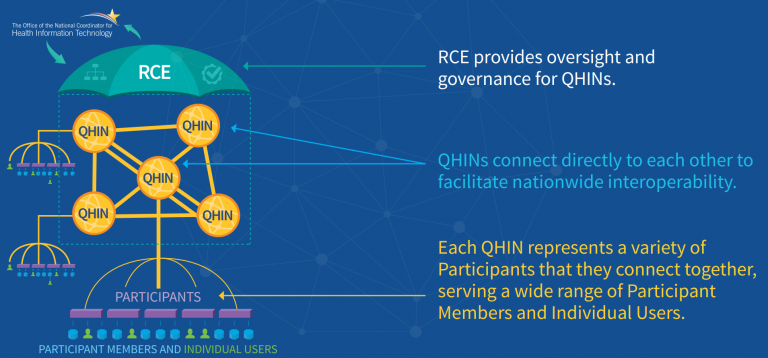
FHIR standardization
Under TEFCA, QHINs will be required to use FHIR-based APIs to exchange health information with other QHINs and healthcare stakeholders. This will ensure that the health information exchanged is standardized, reducing the need for manual data entry and enabling more efficient and accurate data exchange. FHIR APIs will allow the development of new healthcare applications and services that rely on access to health information. For example, healthcare providers can develop new telehealth services or patient engagement tools that depend on access to a patient’s complete medical history.
Common Agreement
The Common Agreement is expected to evolve in 2023. The CA will provide the legal and business terms under which healthcare stakeholders can exchange information and govern the data-sharing practices of healthcare stakeholders. The CA will specify the roles and responsibilities of each stakeholder participating in the national HIE infrastructure, the terms of data sharing, and the necessary safeguards for protecting patient privacy and security.
Implementation
Qualifying healthcare stakeholders are expected to be actively implementing TEFCA throughout 2023. Healthcare providers, payers, and technology vendors will work together to meet the technical and operational requirements of the TEF and sign the CA. This process may involve upgrading or replacing existing healthcare IT systems to meet the technical requirements, as well as developing new workflows and methods for secure and interoperable data sharing. The ONC will be responsible for overseeing the implementation of TEFCA and ensuring that stakeholders comply with all requirements.
Impact
By the end of 2023, TEFCA’s impact is expected to be felt across the healthcare industry. The secure and interoperable exchange of health information is expected to improve patient outcomes, reduce administrative burden, increase efficiency, and unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth. Healthcare providers will be able to access complete medical histories for their patients, leading to better-informed clinical decision-making and improved patient outcomes. Payers will be able to improve their risk adjustment models by having access to more complete and accurate health information. Patients will be able to take a more active role in their healthcare and have greater control over their health information.

What are the benefits of TEFCA?
TEFCA has the potential to bring numerous benefits to the healthcare industry. By establishing a national HIE infrastructure that enables secure and interoperable data sharing, TEFCA can improve patient outcomes, reduce administrative burden, increase efficiency, improve patient engagement, and unlock new business models and services. While TEFCA’s implementation may be complex, the potential benefits are significant and can have a lasting impact on the healthcare industry.
Improved patient outcomes
Providers can make better-informed clinical decisions and coordinate care more effectively by accessing this information, improving patient outcomes, reducing the likelihood of medical errors, and ensuring that patients receive the best possible treatment.
Reduced administrative burden
Standardized health information exchange simplifies the process and reduces the administrative burden on healthcare providers. This can save time and money, reduce the potential for errors, and improve the accuracy of patient data, enabling providers to focus on delivering quality care and improving patient outcomes.
Increased efficiency
Healthcare stakeholders that exchange health information securely and efficiently will reduce the need for manual data entry and duplication of records. This can improve the efficiency of healthcare delivery, save resources, and reduce the time required to make critical decisions.
Improved patient engagement
Better control over personal health information and access to complete medical history can improve patient engagement and allow them to make more informed and active decisions about their care, resulting in better outcomes and greater patient satisfaction.
New business models and services
By enabling EHI’s secure and interoperable exchange, TEFCA can facilitate new business models and services that were not previously possible. Healthcare providers can offer new telehealth services, healthcare applications, and patient engagement tools that rely on access to a patient’s complete medical history, leading to innovation and growth in the industry. Payers can also improve their risk adjustment models by accessing more comprehensive and accurate health information.
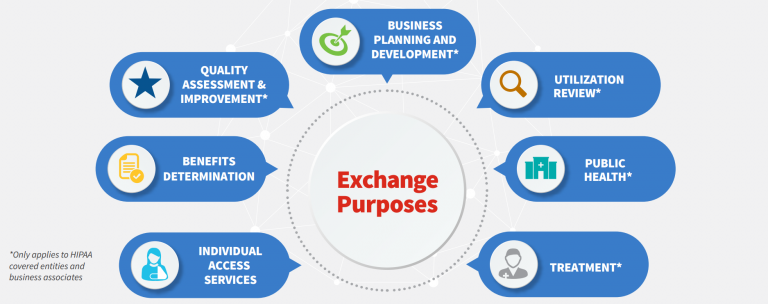
What are the challenges with implementing TEFCA?
While TEFCA has the potential to transform the US healthcare industry by enabling secure and interoperable data sharing, several challenges are associated with its implementation, including complex integration, ensuring data privacy and security, addressing healthcare disparities, and interoperability. These challenges must be addressed to ensure that TEFCA can enable secure and interoperable data sharing in the US healthcare industry over the long term.
Complex implementation
Implementing TEFCA is challenging and requires significant investment in technology and infrastructure. Healthcare stakeholders need to navigate the complex legal and regulatory requirements to upgrade or replace their existing IT systems, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Data privacy and security
TEFCA must ensure that patient data is exchanged securely and in compliance with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and other data privacy regulations. Healthcare stakeholders must establish appropriate policies and procedures to safeguard patient data and ensure it is not misused or disclosed inappropriately.
Interoperability
TEFCA should ensure that healthcare stakeholders can exchange data seamlessly, regardless of the technology platform they are using. This requires the adoption of standardized data elements and exchange protocols and the development of interfaces and data translation services. Ensuring interoperability can be challenging, particularly given the diverse range of IT systems used by healthcare stakeholders.
Conclusion
TEFCA is a critical initiative that has the potential to transform the US healthcare industry by enabling secure and interoperable data sharing. The benefits of TEFCA are numerous, including improved patient outcomes, reduced administrative burden, increased efficiency, and the facilitation of new business models and services. However, TEFCA’s implementation can be complex, and stakeholders may benefit from the expertise of healthcare software development companies to navigate the technical and legal requirements.
Itirra is a Seattle-based healthcare software development company specializing in custom software solutions for health systems, providers, and healthcare companies. With extensive experience in software development, Itirra’s engineers can create specialized solutions that enable TEFCA’s secure and interoperable data sharing, improving patient outcomes, and reducing administrative burdens.
If you’re looking to embrace TEFCA in your healthcare organization, contact us today to learn more about how we can help you with your interoperability needs.

